| To advance
and promote the discipline and professional practice of epidemiology in
Ontario public health units |
 |
| Please click here to visit our new website |

|


 |
| 6B Perinatal Mortality & Stillbirth Rates |
Description | Specific Indicators | Ontario Public Health Standards | Corresponding Health Indicator(s) from Statistics Canada and CIHI | Corresponding Indicator(s) from Other Sources | Data Sources | ICD Codes | Analysis Check List | Method of Calculation | Basic Categories | Indicator Comments | Definitions | Cross-References to Other Indicators | Cited References | Changes Made | Acknowledgements
Description
| - Perinatal mortality: the total number of deaths of a fetus or infant between the end of the 20th week gestation and the end of the 6th day of life in a calendar year per 1,000 total births (live births and stillbirths) in the same calendar year.
- Crude stillbirth rate: the total number of stillbirths per 1,000 total births.
- Stillbirth rate ≥ 500 g: the total number of stillbirths ≥500 g per 1,000 total births.
| | Specific Indicators | - Perinatal mortality rate
- Crude stillbirth rate
- Stillbirth rate ≥ 500 g
| | Ontario Public Health Standards (OPHS) |
The Ontario Public Health Standards (OPHS) establish requirements for the fundamental public health programs and services carried out by boards of health, which include assessment and surveillance, health promotion and policy development, disease and injury prevention, and health protection. The OPHS consist of one Foundational Standard and 13 Program Standards that articulate broad societal goals that result from the activities undertaken by boards of health and many others, including community partners, non-governmental organizations, and governmental bodies. These results have been expressed in terms of two levels of outcomes: societal outcomes and board of health outcomes. Societal outcomes entail changes in health status, organizations, systems, norms, policies, environments, and practices and result from the work of many sectors of society, including boards of health, for the improvement of the overall health of the population. Board of health outcomes are the results of endeavours by boards of health and often focus on changes in awareness, knowledge, attitudes, skills, practices, environments, and policies. Boards of health are accountable for these outcomes. The standards also outline the requirements that boards of health must implement to achieve the stated results.
| | Outcomes Related to this Indicator | - Board of Health Outcome (Reproductive Health): The board of health is aware of and uses epidemiology to influence the development of healthy public policy and its programs and services for the promotion of reproductive health.
- Board of Health Outcome (Foundational Standard): The public, community partners, and health care providers are aware of relevant and current population health information Assessment and/or Surveillance Requirements Related to this Indicator.
| Assessment and Surveillance Requirements Related to this Indicator (Reproductive Health) | - The board of health shall conduct epidemiological analysis of surveillance data... in the area of reproductive health outcomes.
http://www.ontario.ca/publichealthstandards | | Corresponding Health Indicator(s) from Statistics Canada and CIHI | Stillbirth Rate: Total fetal deaths occurring at gestational age of 28 weeks or more per 1000 total births. Perinatal Mortality Rate: Total stillbirths and infant deaths occurring in the first 7 completed days (i.e. 0 - 6 days after birth) per 1000 total births. Under "Health Status, Deaths".
Note that Statistics Canada includes stillbirths ≥28 weeks gestation in their Perinatal Mortality Rate, not ≥20 weeks gestation as per the APHEO Core Indicator definition. http://www.statcan.gc.ca/pub/84f0210x/2008000/technote-notetech1-eng.htm http://www.statcan.gc.ca/pub/82-221-x/2012002/tblstructure/1hs/1de/de1pmx-eng.htm | | Corresponding Indicator(s) from Other Sources | - World Health Organization (WHO) "Stillbirth Rate" definition can be found under "World Health Statistics" - "Mortality and burden of disease" - "Child Mortality": fetus ≥1000 grams or more or ≥28 weeks completed gestation http://apps.who.int/ghodata/
- WHO rates are adjusted estimates produced for the United Nations by the Inter-agency Group for Mortality Estimation (IGME) and are not necessarily the same as official national statistics. For detailed indicator definition, see the latest World Health Statistics Indicators Compendium: http://www.who.int/gho/indicator_registry/en/index.html
- Canadian Perinatal Surveillance System (1):
- Crude Fetal Mortality (Stillbirth) Rate: number of fetal deaths (≥500g or ≥20 weeks gestation) per 1,000 total births.
- Fetal Mortality (Stillbirth) Rate ≥500 g: number of fetal deaths with a birth weight ≥500 g, and if birth weight unknown, with a gestational age ≥22 weeks, per 1000 total births.
Canadian Perinatal Health Report, 2008 | | Data Sources (see Resources: Data Sources) | Note that 3 data sources are listed for use: 1) Vital statistics, 2) Hospitalization, 3) BORN. The choice of data source will depend upon data quality within a health unit as well as data access and the specific analysis questions. For information related to the data sources, refer to the Data Source resources and the Reproductive Health Core Indicators Documentation Report. | | Alternative 1: | Numerator:
Vital Statistics Stillbirth Data
Original source: Vital Statistics, Ontario Office of Registrar General (ORG)
Distributed by: Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care (MOHLTC): IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO (IntelliHEALTH)
Suggested citation (see Data Citation Notes): Ontario Stillbirth Data [years], Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO, Date Extracted: [date].
Vital Statistics Mortality Data
Original source: Vital Statistics, Ontario Office of Registrar General (ORG)
Distributed by: Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care (MOHLTC): IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO (IntelliHEALTH)
Suggested citation (see Data Citation Notes): Ontario Mortality Data [years], Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO, Date Extracted: [date].
Denominator:
Vital Statistics Live Birth Data
Original source: Vital Statistics, Ontario Office of Registrar General (ORG)
Distributed by: Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care (MOHLTC): IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO (IntelliHEALTH)
Suggested citation (see Data Citation Notes): Ontario Vital Statistics Live Birth Data [years], Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO, Date Extracted: [date]. Vital Statistics Stillbirth Data
Original source: Vital Statistics, Ontario Office of Registrar General (ORG)
Distributed by: Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care (MOHLTC): IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO (IntelliHEALTH)
Suggested citation (see Data Citation Notes): Ontario Mortality Data [years], Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO, Date Extracted: [date]. | | Alternative 2: | Numerator & Denominator: Hospitalization Data
Original source: Discharge Abstract Database (DAD), Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI)
Distributed by: Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care (MOHLTC): IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO (IntelliHEALTH)
Suggested citation (see Data Citation Notes): Inpatient Discharges [years], Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, IntelliHEALTH ONTARIO, Date Extracted: [date]. | | Alternative 3 | Numerator & Denominator: BORN Information System
Original source: Better Outcomes Registry Network (BORN) Ontario
Distributed by: Better Outcomes Registry Network (BORN) Ontario
Suggested citation (see Data Citation Notes): BORN Information System [years], Date Extracted: [date].
| ICD-10 Codes
| | Stillbirth | - Maternal complications of pregnancy: (ICD-9: E761); (ICD-10-CA: P01)
- Complications of placenta/cord/membranes: (ICD-9: E762); (ICD-10-CA: P02)
- Intrauterine hypoxia and birth asphyxia: (ICD-9: E768); (ICD-10-CA: P20; P21)
- Unspecified: (ICD-9: 779.9); (ICD-10-CA: P95; P96.9)
- Congenital anomalies: (ICD-9: 740-759); (ICD-10-CA: Q00-Q99)
| | Neonatal Death | - All causes
- All accidental deaths: (ICD-9: E800-E999); (ICD-10-CA: V01-Z99)
- Homicide/infanticide: (ICD-9: E960-E969); (ICD-10-CA: X85-Y09)
- Shaken Baby Syndrome: (ICD-9: 850-854 with E967); (ICD-10-CA: S06 with Y07)
- Child battery and maltreatment or criminal neglect: (ICD-9: E967 & E968.4); (ICD-10-CA: Y06-Y07)
- Falls: (ICD-9: E880-E888); (ICD-10-CA: W00-W19)
- RDS: Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ICD-9: 769.0-769.9); (ICD-10-CA: P22)
- SIDS: Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (ICD-9: 798.0); (ICD-10-CA: R95)
- Congenital anomalies: (ICD-9: 740-759); (ICD-10-CA: Q00-Q99)
- Low birth weight (not short gestation): (ICD-9: 764); (ICD-10-CA: P05)
- Low birth weight with short gestation: (ICD-9: 765); (ICD-10-CA: P07)
- Intrauterine hypoxia and birth asphyxia: (ICD-9: 768); (ICD-10-CA: P20 & P21)
- Other conditions of the perinatal period: (ICD-9: 760-764, 766, & 770-779); (ICD-10-CA: P00-P04, P08, & P23-P96)
- Pneumonia and influenza (ICD-9: 480-487); (ICD-10-CA: J10-J18)
- Certain gastrointestinal diseases (ICD-9: 008-009, 535, & 555-558); (ICD-10-CA: A00-A09, K29, K50-K52, K55-K63)
| | Analysis Check List | - The IntelliHEALTH licensing agreement does not require suppression of small cells, but caution should be used when reporting at a level that could identify individuals, (e.g. reporting at the postal code level by age and sex). Please note that privacy policies may vary by organization. Prior to releasing data, ensure adherence to the privacy policy of your organization.
- Aggregation (e.g. combining years, age groups, categories) should also be considered when small numbers result in unstable rates.
- Analyze mortality data by infant residence, not place of death. Analyze stillbirth data by mother's residence.
- For detailed information about live birth and stillbirth data provided in by the Ontario Registrar General, refer to Vital Statistics Live Births and Vital Statistics Stillbirths resources.
- HELPS Data: Historically, PHUs obtained data for live births, stillbirths, therapeutic abortions, congenital anomalies, and deaths from the Ministry of Health through HELPS (the HEalthPlanning System). Although these data are no longer commonly used, some PHUs may still be accessing these data files. Information about the data can be found in the HELPS Data Source resource.
| | Vital Statistics - Mortality Data: | - Use Deaths data source from the Vital Statistics folder in IntelliHEALTH, select #ON Deaths measure (number of deaths for Ontario residents who died in Ontario). Note: deaths for Ontario residents who died outside the province are not captured in Vital Statistics.
- Select appropriate geography from Deceased Information folder (public health unit or LHIN). Include other items, depending on your requirements (ICD10 Chapter, Lead Cause Group, age group, sex, etc.).
- In mortality data set, External Cause of Injury Codes (ICD10 V-Y; ICD9 E-Codes), and not Injury & Poisoning Codes (ICD20S-T codes; ICDD9 800 - 999 codes) are used in assigning primary cause of death. ICD-9 Chapter Primary Cause of death is available from C1986 to C1999, excludes Chap. 17 - Nature of Injury codes (never underlying cause) - includes Chap. 19 - External Causes.
| | Vital Statistics - Live Birth Data: | - Use Birth Summary data source under Vital Statistics information map.
- Select a measure under Measures data item. "# Births" gives the number of births (live births & stillbirths) to Ontario mothers who gave birth in ON excluding ON mothers who gave birth outside ON and "# LB" gives the number of live births.
- When selecting Maternal PHU, exclude births to "out-of-province" mothers.
- "Birth Type" under Birth Information may be used to select whether the birth is singleton, twin, or other.
| | Vital Statistics - Stillbirth data: | - Use Stillbirth data source under Vital Statistics information map
- Under "Measures" data item, select "#SB(ON Res)" to obtain the number of stillbirths to mothers who resided in ON and gave birth in ON which excludes ON mothers who gave birth outside ON.
| | Hospitalization Data: | - Under the Inpatient Discharge Main Table data source from the ‘05 Inpatient Discharges' folder, use the "Hospital Births-newborns, stillborns" predefined report. This report can be modified, renamed and saved under your own folder.
- The report provides hospital birth counts (Admit Entry Type = N for Newborn or S for Stillbirth) for Ontario and by PHU, including only Ontario residents (Patient Province equal to ON).
- The calendar year for date of admission is used (Admit CYear) rather than date of discharge since the date of admission will be the same as the birthdate.
- Even though counts are grouped by calendar year of admission, it is the actual number of discharges that is counted.
- Select the appropriate calendar years, PHU, and "Newborn - Born Alive in Reporting Institution" and/or "Stillborn Infant born in Reporting Institution.
- Birth weight is not available in hospitalization data for stillbirths; as a result only the crude stillbirth rate can be calculated and not the stillbirth rate ≥500 g. Counts of stillbirths are available as of the 2003 calendar year.
| | BORN Data | | | Method of Calculation | | Perinatal Mortality Rate | total number of stillbirths & deaths in infants 6 days of age or younger | x 1,000 |
| total number of births (live births & stillbirths) |
Crude -Stillbirth Rate | total number of stillbirths | x 1,000 |
| total number of births (live births & stillbirths) |
Stillbirth Rate ³ 500 g | total number of stillbirths ³ 500 g | x 1,000 |
| total number of births ³ 500 g (live births & stillbirths) |
| | Basic Categories | - Geographic areas of patient residence:
- Vital Statistics, Hospitalization data: Ontario, public health unit, municipality, and smaller areas of geography based on aggregated postal code
- BORN data: Ontario, public health unit
- Age of mother, gestational age, birth weight, sex
- Specific cause of death
| | Indicator Comments | | | Definitions | | Components of Fetal-Infant Mortality | 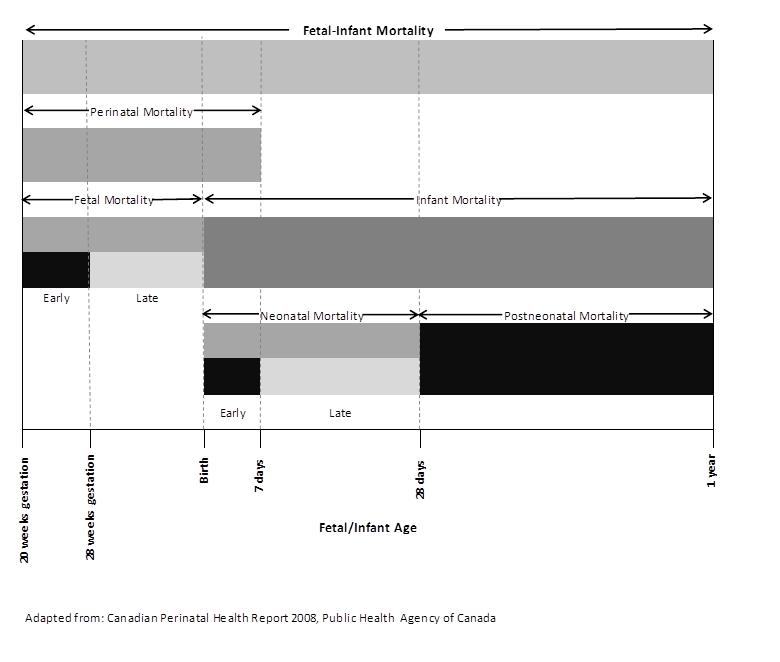 | | Cross-References to Other Indicators | | | Cited References | Public Health Agency of Canada. Canadian Perinatal Health Report. 2008 Edition. Ottawa, 2008 - World Health Organization. Neonatal and Perinatal Mortality: Country, Regional and Global Estimates. 2006. Available from: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241563206_eng.pdf
- Spong CY, Iams J, Goldenberg R, Hauck FR, Willinger M. Disparities in perinatal medicine: preterm birth, stillbirth and infant mortality. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117(4):948-55.
- Zhong-Cheng L, Senecal S, Simonet F, Guimond E, Penney C, Wilkins R. Birth outcomes in the Inuit-inhabited areas of Canada. CMAJ. 2010;182(3):235-42.
- Woodward GL, Ardal S. Data Quality Report: Effect of Residence Code Errors on Fertility Rates. Central East Health Information Partnership, July 2000.
- Bienefeld M, Woodward GL, Ardal S. Underreporting of live births in Ontario: 1991-1997. Central East Health Information Partnership, February 2001.
- Joseph KS, Kramer MS. Recent trends in Canadian infant mortality rates: the effect of changes in registration of live newborns weighing less than 500g. Can Med Assoc J 1996; 155:1047-52.
| | Changes Made | Date | Type of Review-Formal Review or Ad Hoc? | Changes made by | Changes | August 13, 2012 - January 16, 2013 | Formal Review | Reproductive Health Sub-Group | - All sections updated in alignment with the Guide to Creating or Editing Core Indicator pages
- Updated the indicator definition. Added Stillbirth rate ≥500 g to the Specific Indicators and removed Perinatal Mortality Ratio.
- Three data sources cited with analysis check-list for each.
- Updated Corresponding Indicators from Other Sources, Method of Calculation, Indicator Comments, Cited References.
| | February 22, 2013 | Ad Hoc | Reproductive
Health Sub-
Group | - Method of calculation for "Stillbirth Rate ³ 500 g":
changed the denominator to "total number of births ³ 500 g"
from "total number of births"
|
| | Acknowledgements | Lead Author(s) | - Natalie Greenidge, Public Health Ontario
- Carol Paul, Ontario Ministry of Health and Long Term Care
- Enayetur Raheem, Windsor Essex County Health Unit
- Nancy Ramuscak, Peel Public Health
| Contributing Author(s) | - Reproductive Health Sub-group
| Reviewers | - Ahalya Mahendra, Public Health Agency of Canada (Core Indicators Work Group Member)
- Virginia McFarland, Grey Bruce Health Unit
- Paula Stewart, Leeds Grenville and Lanark District Health Unit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|